Supply Chain Management (SCM) is a set of various activities in which raw materials are purchased and transformed into semi-finished or intermediate goods, which eventually become the finished goods. These finished goods are then distributed to the customer using the distribution channel. This complete cycle from supplier to customer is called the Supply Chain Management process.
The need for SCM is because effective Supply Chain Management is the next logical step towards increased profits and market share. So effective management of SCM components plays a important role in the dynamics of business
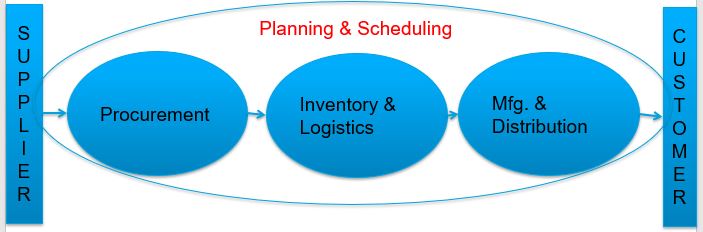
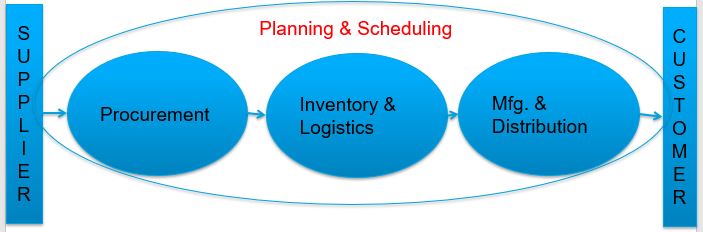
Supply Chain Management (SCM) in line manager prospective is “let’s-keep-things-moving-efficiently”. Moreover, SCM involves seamless flow of material, information & finance in a network consisting of customers, suppliers, manufacturers, retailers and distributors.
SCM has three primary goals:
- Reduce inventory
- Increase the transaction speed by exchanging data in real-time
- Increase sales by implementing customer requirements more efficiently.
Table of Contents
Supply Chain Management Elements
A supply chain is a network of
- suppliers
- manufacturing
- warehouse
- distribution
- logistics facilities
- customers.
Product flow happens in a supply chain from supplier to manufacturer to distributor to retailer to customer where as cash & information flow happens in the reverse direction.
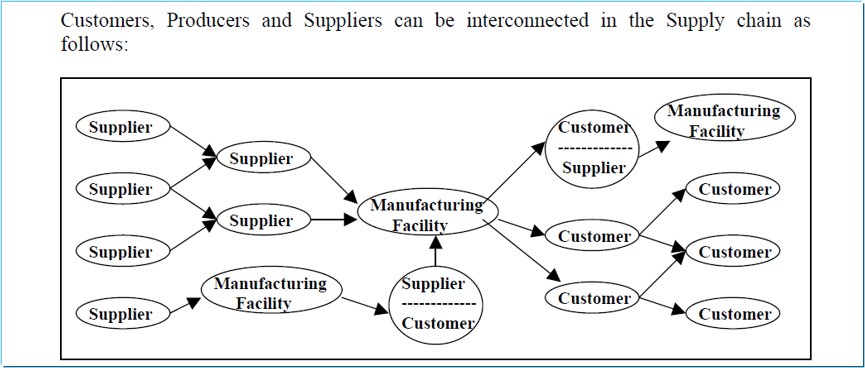
Key elements in Supply Chain Management:
- Customers
- Producers (includes Retailer, Distributor, Manufacturer)
- Suppliers
Inter-relationship of the elements
- A number of companies can be linked in the supply chain network.
- A supplier to one manufacturing facility can be a customer to another manufacturing facility and so on.. hence a number of supplier / customer relationships exist in the supply chain network.
- A number of intermediaries (distributors, wholesalers, retailers etc.,) form part of the supply chain network.
Following are eight Key areas of supply chain management
- Design
- Market
- Plan
- Sell
- Procure
- Manufacture
- Fulfill
- Service and Maintain
For better understanding from Product point, let’s understand on eight key areas as given above
- Design : SCM start with designing & developing new products where Product specifications are created. Few Important applications play major role in this phase.
- Oracle Product Life cycle Management
- Oracle Advanced product Catalog
- Engineering & Bills of Materials
- Market : Marketing and Sales generates demand for the Product by publicizing its features and how it would address customer priorities. In the process, Marketing also gets customer feedback and communicates to Product development group. These are application potentially can be used
- Telesales
- Trade Management
- Incentive Compensation
- Order Capture
- Oracle sales
- Plan: Planning is the strategic portion of SCM. You need a strategy for managing all the resources that go toward meeting customer demand for your product or service.
- Advanced Supply Chain Planning
- Global Order Promising
- Sell & Manage Order: Maintain and manage the customer orders, order holds, notes and release the orders to warehouse for fulfillment based on requested date, product availability and customer credit limit.
- Order management
- Advanced Pricing
- Configurator
- i-Store
- Procure: Here you normally choose the suppliers that will deliver the goods and services you need to create your product. Develop a set of pricing, delivery and payment processes with suppliers and create metrics for monitoring and improving the relationships.
- Purchasing
- i-Procurement
- Manufacture: Schedule the manufacturing activities necessary for production, testing, packaging and preparation for delivery.
- Cost Management
- Process Manufacturing
- Project Manufacturing
- Quality
- Work in Process
- Fulfill & Release Management: Coordinate the receipt of orders from customers, develop a network of warehouses, pick carriers to get products to customers and set up an invoicing system to receive payments.
- Shipping Execution
- Inventory Management
- Warehouse Management System
- Transportation Execution
- Service & Maintain: Create a network for receiving defective and excess products back from customers and supporting customers who have problems with delivered products.
- Depot Repair
- Field Service
- Install Base
- Service Contracts
Oracle SCM Business Processes Lifecycles
SCM Processes can be fit in Oracle applications called as business process lifecycles . Some of the important Business Process lifecycles are explained in brief as below.
Procure to Pay (P2P)
- Procure to pay lifecycle captures demands from different applications like Inventory, Order Management, Purchasing & consolidate all demands in the form of requisitions.
- Requisitions can be optionally converted in to RFQ & Quotations, or else directly converted in Purchase Orders. Approved PO then can be send to suppliers & receipts are generated in different Inventory organizations.
- Further more Financials applications can be used to capture invoices & process payments for suppliers.
Order to Cash (O2C)
- O2C lifecycle starts with entering different types of orders on to customer’s name. Book orders once all relevant scheduling & pricing information of item is reviewed
- Booked orders are treated as firm demand to process orders either for manufacturing or fulfilling the demand through supplier networks.
- Then you Pick release & ship confirms these orders to interface data with accounts Receivables for further financial transactions.
Lead to Service
- A lead is an expressed customer interest that a sales agent uses to determine whether there is potential for a after sales service opportunity.
- Leads are intended to capture the initial contact with potential or existing customers, gathering just enough information to tell a sales organization whether there is sufficient interest on behalf of the buyer to make a lead worth following up.
Forecast to Plan
- This business flow outlines how a company uses sales order history to produce a forecast, design a production, manufacturing, or distribution plan from that forecast, and how to analyze, revise, and simulate changes to that plan.
Demand to Build
- This business flow outlines how a company analyzes or anticipates demand and translates that demand to a production plan.
On a whole, oracle provides two streams to capture entire supply chain planning
- Manufacturing: Consists of Inventory, Bills of Material & Work in Process to capture details of every type of manufacturing like discrete, batch, mass production.
- Distribution: Consists of Inventory, Purchasing, and Order Management to capture entire procure to pay & order to cash business processes.
On a summary note, Oracle E-Business Suite, does cover each area of SCM as discussed above. The supply chain encompasses all activities associated with the flow and transformation of goods from the raw materials stage (extraction), through to end users, as well as the associated information flows.
Material and information flows both up and down the supply chain. The supply chain includes new product development, systems management, operations and assembly, purchasing, production scheduling, order processing, inventory management, transportation, warehousing, and customer service.
Supply chains are essentially a series of linked suppliers and customers; every customer is in turn a supplier to the next downstream organization until a finished product reaches the ultimate end user.