Table of Contents
Overview of VB Script
VBScript is a Microsoft scripting language.It is the default scripting language in ASP.
VBScript is a scripting language is a lightweight programming language.
It is a light version of Microsoft’s programming language Visual Basic
It is only supported by Microsoft’s browsers (Internet Explorer)
It uses the Component Object Model to access elements of the environment
VB Scripting Syntax and Guidelines
VBScript is used to develop scripts to perform both simple and complex object-based tasks
The following general VBScript syntax rules and guidelines:
- Case-sensitivity – VBScript is not case sensitive by default .
For example :
The two statements are identical in VBScript.
Browser(“Mercury”).Page(“Find a Flight:”).WebList(“toDay”).Select “31”
browser(“mercury”).page(“find a flight:”).weblist(“today”).select “31” - Text strings – When you enter a value as a text string, you must add quotation marks before and after the string.
- Variables – Used to store strings, integers, arrays and objects .
- Parentheses – To achieve the desired result and to avoid errors, we use parentheses () correctly in your statements.
- Comments – Comments are added wherever possible, to make your scripts easier to understand and maintain.
- Spaces – Spaces are ignored by VBScript and it improve clarity.
VB Script – Constants
A constant is a meaningful name that takes the place of a number or string and never changes. There are number of useful constants built-in Vbscript
The various categories of constants in VBScript.
- Color Constants
- Date and Time Constants
- Date Format Constants
- Miscellaneous Constants
- MsgBox Constants
- String Constants
- Tristate Constants
- VarType Constants
VB Script – Color Constants
Color Constants – Defines about the eight basic colors that can be used in scripting.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbBlack | &h00 | Black |
| vbRed | &hff | Red |
| vbGreen | &hff00 | Green |
| vbYellow | &hffff | Yellow |
| vbBlue | hff0000 | Blue |
| vbMagen | &hff00ff | Magen |
| vbCyan | &hffff00 | Cyan |
| vbWhite | &hffffff | White |
VB Script – Date and Time Constants
Date and Time : Defines about the date and time constants used by various date and time functions.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbSunday | 1 | Sunday |
| vbMonday | 2 | Monday |
| vbTuesday | 3 | Tuesday |
| vbWednesday | 4 | Wednesday |
| vbThursday | 5 | Thursday |
| vbFriday | 6 | Friday |
| vbSaturday | 7 | Saturday |
VB Script – Date Format Constants
| Constant | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| vbGeneralDate | 0 | Display a date and/or time. Date and time display is determined by system settings. |
| vbLongDate | 1 | Display a date using the long date format as per computer settings. |
| vbShortDate | 2 | Display a date using the short date format as per computer’s regional settings. |
| vbLongTime | 3 | Display a time using the long time format as per computer settings. |
| vbShortTime | 4 | Display a time using the short time format as per computer’s regional settings. |
VB Script – Errors
The Error that occur during the execution are classified into :
- VB Script runtime errors
- VB Script syntax errors
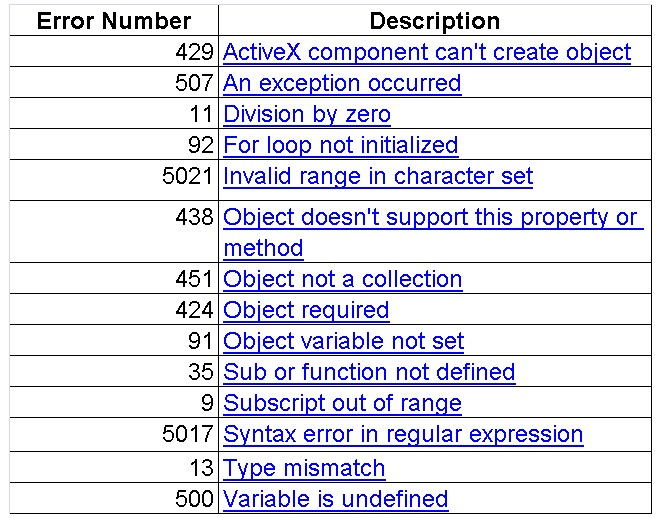
VB Script – Runtime Error
Runtime error – Unexpected errors that causes hindrance during the execution of scripts
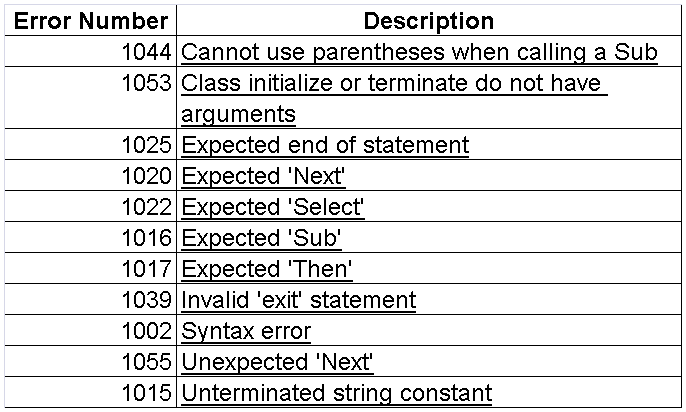
VB Script – Syntax errors
Syntax error – The error that results when the structure of one of your VBScript statements violates one or more of the grammatical rules of the VBScript scripting language.
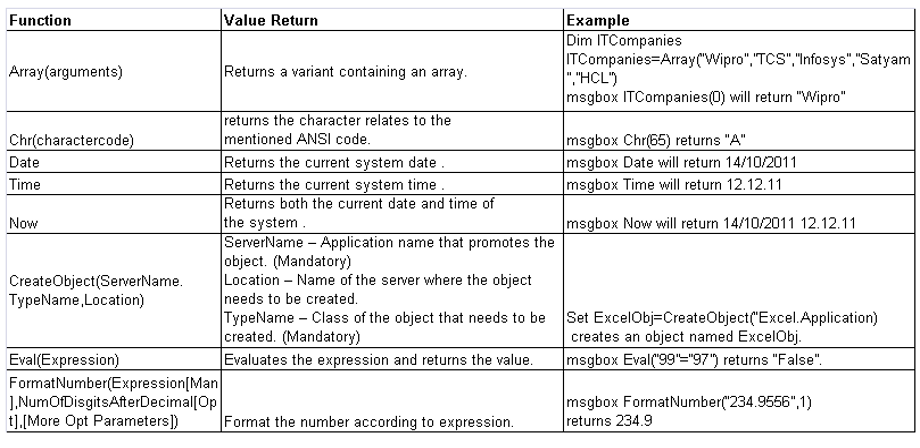
VB Script – Functions
VB Script supports some well/pre defined functions for easy manipulations.Below pointers are some of the important functions.
VB Script – Keywords
| Function | Value Return | Example |
| Empty | Used to indicate an uninitialized variable value. A variable value is uninitialized when it is first created and no value is assigned to it, or when a variable value is explicitly set to empty. |
Dim Captain , Captain=“Dhoni”, Captain=Empty |
| Nothing | Used to indicate an uninitialized object value, or to disassociate an object variable from an object to release the system resources |
Set ExcelOb=CreateObject(“Excel.Application”) , Set ExcelOb=Nothing. |
| Null | Used to indicate that the variable has no data. |
x = Null , x contains no valid data |
VB Script – Methods
| Function | Value Return | Example |
| Clear | Clears all the existing property values for the “err”. | Object.clear, On error resume next ; err.raise=6 ; err.clear ; msgbox err.number will return 0. |
| Replace Method | Replaces the text found in an regular expression search. | object.Replace(string1, string2) , Example : ReplaceTest = regEx.Replace(str1, replStr) |
| Execute | Executes a regular expression search against a string. | object.Execute(Str) -, Example : Var1 = 1,Var2 = 2;Execute(“Var1 = Var2 + 3”) Response.Write (Var1) will print 5. |
VB Script – Operators
VBScript’s operators can be separated into four semi-distinct categories.
Math Operators
| Operator | English | Example | Result |
| + | Addition | 1+1 | 2 |
| – | Subtraction | 2-1 | 1 |
| * | Multiplication | 4*4 | 16 |
| / | Division | 4/2 | 2 |
| ^ | Exponent | 2^3 | 8 |
| mod | Modulus | 4 mod 3 | 1 |
Comparison Operators
| Operator | English | Example | Result |
| = | Equal to | 10=11 | False |
| > | Greater than | 10>9 | True |
| < | Lesser than | 9<8 | False |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | 4>=2 | True |
| <= | Lesser than or equal to | 2<=3 | True |
| <> | Not equal to | 4 <> 3 | False |
String Operators
| Operator | English | Example | Result |
| & | Connected to | “Treno”&”vision” | Trenovision |
Logical Operators
| Operator | English | Example | Result |
| AND | Both must be true | True and True | True |
| OR | Either on must be true | True and False | True |
| NOT | Inverse of Truth | Not False | True |
VB Script – Statements (Looping)
Looping statements are used to run the same block of code a specified number of times.
| Function | Value Return | Example |
| For…Next statement | Use the For…Next statement to run a block of code a specified number of times | For i=0 to 2 msgbox “Wipro” End For ‘ will print Wipro three times. |
| For Each…Next Loop | A For Each…Next loop repeats a block of code for each item in a collection, or for each element of an array. | Cars=array(“Mercedez”,”Jaguar”) For each y in cars msgbox y Next ‘ Will print Mercedez and then Jaguar. |
| Do…Loop statement | The Do…Loop statement repeats a block of code while a condition is true, or until a condition becomes true. |
Do While i>5 ‘some code Loop ‘ If i=4 , it will never get executed , if i=7 it will get executed until the ‘some code’ part return a value less than 5 |
| While…Wend statement | Executes a series of statements as long as a given condition is True. |
i=4 ,While i<5 msgbox “printed” i=6 Wend ‘ will print “printed” once in a message box. |
VB Script – Conditional Statements
Conditional statements are used to perform different actions for different decisions.In VBScript we have four conditional statements:
| Function | Value Return | Example |
| If statement | executes a set of code when a condition is true | Dim Cricketer , Cricketer=“Dhoni” If Cricketer=“Dhoni” Then msgbox “Top Ranking Player” End if. |
| If…Then…Else statement | Select one of two sets of lines to execute | Dim Mark , Mark=“50” If Mark>=“50” Then Msgbox “Pass” Else msgbox “fail” end if |
| If…Then…ElseIf statement | select one of many sets of lines to execute | Dim State , State=“Pass” If State=“Pass” Then msgbox “1” ElseIf State=“Fail” Then msgbox “0” Else msgbox “The entered state is other than Pass or Fail” End If |
| Select Case statement | select one of many sets of lines to execute | Dim MonthInt, MonthInt=2 Select Case(MonthInt) Case “1” msgbox “January” Case “2” msgbox “February” Case else msgbox “Enter either 1 or 2” End Select |
For Reference
http://www.irt.org/articles/js117/
http://www.tizag.com/vbscriptTutorial/
http://www.onestopqa.com/resources/VB%20Script%20Basics.pdf
http://www.quackit.com/vbscript/tutorial/


